Pipeline Construction and Maintenance: A Comprehensive Guide to Industry Best Practices
Introduction to Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Pipeline construction and maintenance represent critical components of global infrastructure development. These complex systems serve as the lifelines for transporting vital resources including oil, natural gas, water, and chemicals across vast distances. The importance of proper pipeline construction and maintenance cannot be overstated, as these networks ensure the safe, efficient, and environmentally responsible delivery of resources that power industries and communities worldwide.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the intricate world of pipeline construction and maintenance, examining everything from initial planning and design considerations to cutting-edge techniques for ensuring operational integrity. Whether you’re an industry professional seeking to enhance your knowledge or a stakeholder looking to understand the complexities of pipeline infrastructure, this resource provides valuable insights into the standards, technologies, and practices that define excellence in the field.

The Evolution of Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
The history of pipeline construction and maintenance spans centuries, with significant technological advancements transforming what was once rudimentary infrastructure into sophisticated systems. Early pipeline networks, often constructed from wood or basic metals, have evolved into highly engineered structures capable of withstanding extreme conditions and transporting materials safely over thousands of miles.
Pipeline construction and maintenance methodologies have progressed dramatically in recent decades. Modern approaches incorporate advanced materials science, digital monitoring systems, and preventative maintenance protocols that extend operational lifespans while minimizing environmental impacts. This evolution reflects the industry’s ongoing commitment to safety, efficiency, and sustainability.
Key Planning Considerations for Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Before any physical work begins, thorough planning establishes the foundation for successful pipeline construction and maintenance. This critical phase involves multiple considerations:
Regulatory Compliance in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Pipeline construction and maintenance projects must navigate complex regulatory frameworks that vary by region and industry sector. These regulations typically address safety standards, environmental protections, and operational requirements. Successful projects begin with comprehensive regulatory analysis and continue with documentation systems that ensure compliance throughout the pipeline’s lifecycle.
Environmental Impact Assessment for Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Environmental considerations play an increasingly prominent role in pipeline construction and maintenance planning. Comprehensive environmental impact assessments identify potential concerns and inform mitigation strategies. These assessments typically examine factors including habitat disruption, water quality protection, emissions control, and restoration requirements.
Route Selection for Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
The pathway chosen for pipeline installation significantly influences construction complexity, maintenance requirements, and overall project viability. Optimal route selection balances factors including topography, soil conditions, population density, environmental sensitivity, and access for future maintenance activities. Geographic information systems (GIS) and advanced mapping technologies have revolutionized this aspect of pipeline construction and maintenance planning.

Stakeholder Engagement in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Effective communication with communities, landowners, regulatory agencies, and other stakeholders represents a crucial element of pipeline construction and maintenance planning. Proactive engagement helps address concerns, secure necessary permissions, and establish positive relationships that facilitate both initial construction and ongoing maintenance activities.
Materials Selection for Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
The materials chosen for pipeline systems directly impact performance, longevity, and maintenance requirements. Selection must consider multiple factors:
Steel Specifications for Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Steel remains the predominant material for major pipeline construction and maintenance projects, particularly for oil and gas applications. Material specifications consider pressure ratings, temperature ranges, corrosion resistance, and mechanical properties. Advances in metallurgy continue to enhance the performance capabilities of pipeline steel, with high-strength variants offering improved durability with reduced material requirements.
Composite Solutions in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) and other composite materials have gained popularity in certain pipeline construction and maintenance applications. These alternatives offer advantages including corrosion resistance, lightweight installation, and in some cases, lower lifetime maintenance costs. Composite solutions prove particularly valuable in chemically aggressive environments where traditional materials might degrade quickly.
Coating Systems for Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Protective coatings represent a critical component of pipeline construction and maintenance strategies. These systems provide barriers against corrosion, mechanical damage, and environmental stressors. Modern coating technologies include fusion-bonded epoxies, polyethylene, and multi-layer systems designed to address specific operational challenges and extend service life.
Joining Methods in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
The techniques used to connect pipeline segments significantly impact system integrity. Welding remains the primary joining method for steel pipelines, with strict quality control protocols ensuring structural soundness. Alternative joining methods, including mechanical couplings and adhesive bonding for composite systems, play important roles in specific pipeline construction and maintenance scenarios.
Excavation and Site Preparation for Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Proper groundwork creates the foundation for successful pipeline construction and maintenance:
Soil Analysis for Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Understanding soil characteristics informs multiple aspects of pipeline construction and maintenance. Geological surveys assess factors including soil stability, drainage properties, chemical composition, and frost susceptibility. These analyses guide decisions regarding excavation methods, trench design, backfill materials, and long-term monitoring requirements.
Trenching Techniques in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Pipeline construction and maintenance projects employ various trenching approaches depending on terrain, pipeline diameter, soil conditions, and environmental factors. Methods range from conventional open-cut excavation to specialized techniques like rock trenching and microtrenching. Proper trench design addresses issues including depth requirements, sidewall stability, and bedding materials.
Horizontal Directional Drilling in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Horizontal directional drilling (HDD) has revolutionized pipeline construction and maintenance, particularly for water crossings and urbanized areas. This trenchless methodology minimizes surface disruption while enabling pipeline installation beneath obstacles. HDD planning involves detailed geotechnical investigation and specialized equipment selection to ensure successful execution.
Dewatering Strategies for Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Managing groundwater represents a significant challenge in many pipeline construction and maintenance operations. Effective dewatering approaches may incorporate techniques including wellpoint systems, submersible pumps, and groundwater cutoff methods. Proper water management protects both the construction environment and the integrity of newly installed pipeline components.
Installation Techniques in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
The physical installation phase demands precision and adherence to established methodologies:
Pipe Handling and Stringing in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Proper handling of pipeline materials prevents damage that could compromise long-term performance. Pipeline construction and maintenance operations typically employ specialized equipment for transporting, unloading, and positioning pipe segments. Strategic positioning of materials along the right-of-way (stringing) optimizes workflow efficiency during the installation process.
Welding Standards for Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Welding operations form the literal backbone of steel pipeline construction and maintenance. Industry standards specify qualification requirements for welders, acceptable procedures, and quality verification methods. Advanced technologies, including automated welding systems and phased array ultrasonic testing, enhance quality control in modern pipeline construction and maintenance projects.
Lowering-In Procedures for Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
The process of placing assembled pipeline segments into prepared trenches requires careful coordination and specialized equipment. Proper lowering-in techniques in pipeline construction and maintenance prevent damage to both the pipe and its protective coatings. Side booms, vacuum lifters, and roller cradles represent common tools employed during this critical phase.
Backfilling Methods in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Proper backfilling protects the installed pipeline and restores site conditions. Pipeline construction and maintenance specifications typically detail requirements for bedding materials, compaction standards, and restoration techniques. Specialized approaches may be necessary in environmentally sensitive areas or locations with unstable soil conditions.
Testing and Commissioning in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Verification procedures ensure system integrity before operational startup:
Hydrostatic Testing in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Pressure testing represents a fundamental quality verification method in pipeline construction and maintenance. Hydrostatic testing identifies potential leaks or structural weaknesses before a pipeline enters service. Testing protocols specify pressure levels, duration, temperature considerations, and acceptance criteria based on regulatory requirements and industry standards.
Geometric Inspection for Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Pipeline geometry verification has become an increasingly important component of pipeline construction and maintenance. In-line inspection tools, often called “geometry pigs,” identify dents, ovality issues, and other deformations that might affect flow characteristics or structural integrity. These inspections establish baseline conditions for future maintenance comparisons.
Cathodic Protection Verification in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Corrosion protection systems require thorough testing during pipeline construction and maintenance operations. Verification procedures confirm proper installation of anodes, rectifiers, test stations, and electrical isolation components. Initial potential surveys establish baseline protection levels that guide future maintenance activities.
Documentation Requirements for Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Comprehensive documentation provides the foundation for future pipeline construction and maintenance activities. As-built records document the pipeline’s precise location, materials used, test results, and special considerations. These records prove invaluable for subsequent integrity management, regulatory compliance, and maintenance planning.
Preventative Maintenance Strategies for Pipeline Infrastructure
Proactive approaches extend service life and prevent costly failures:
Risk-Based Inspection in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Modern pipeline construction and maintenance programs employ risk assessment methodologies to prioritize inspection activities. These approaches identify pipeline segments with elevated vulnerability based on factors including age, operating conditions, environmental exposure, and consequence of failure. Risk-based inspection optimizes resource allocation while maintaining system integrity.
Corrosion Monitoring in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Corrosion represents one of the primary threats to pipeline integrity. Effective pipeline construction and maintenance programs incorporate multiple monitoring techniques, including close-interval potential surveys, coupon testing, electrical resistance probes, and regular visual inspection at test points. Data from these monitoring activities informs maintenance prioritization.
Cathodic Protection Maintenance for Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Impressed current and sacrificial anode systems require ongoing attention as part of pipeline construction and maintenance programs. Regular monitoring confirms adequate protection levels, while periodic adjustments compensate for anode consumption, coating deterioration, and changing environmental conditions. Comprehensive cathodic protection maintenance extends pipeline service life significantly.
Right-of-Way Management in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Proper corridor maintenance facilitates both inspection activities and emergency response in pipeline construction and maintenance. Vegetation management, erosion control, and access maintenance represent ongoing responsibilities. Regular aerial and ground patrols identify potential threats from unauthorized excavation, natural forces, or other external factors.
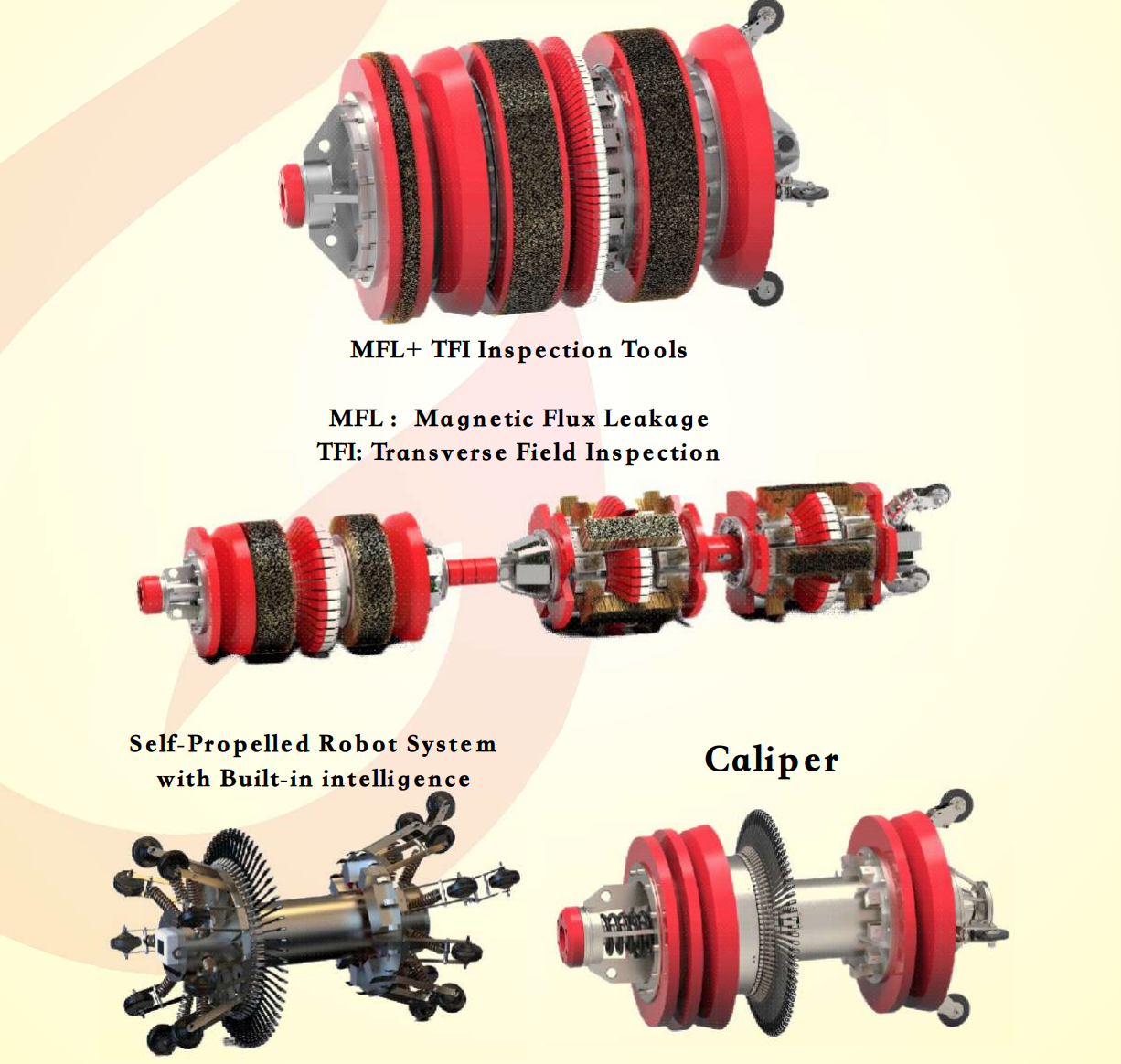
In-Line Inspection Technologies for Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Advanced tools provide detailed condition assessment without service interruption:
Magnetic Flux Leakage in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Magnetic flux leakage (MFL) technology has become a cornerstone of pipeline construction and maintenance programs. These inspection tools detect metal loss from corrosion, gouging, or manufacturing defects. Advanced MFL systems offer increasingly precise characterization of anomalies, enabling more accurate maintenance planning.
Ultrasonic Inspection for Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Ultrasonic tools provide complementary capabilities in pipeline construction and maintenance assessment. These systems excel at detecting and measuring crack-like defects, laminations, and wall thickness variations. Phased array ultrasonic technology offers enhanced resolution for critical pipeline segments where precise defect characterization is essential.
Caliper Tools in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Deformation assessment represents an important component of pipeline construction and maintenance programs. Caliper tools identify and measure dents, ovality, wrinkles, and other geometric irregularities that might affect flow efficiency or structural integrity. These tools often incorporate multiple sensor technologies for comprehensive assessment.
Data Integration Systems for Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Modern pipeline construction and maintenance approaches incorporate sophisticated data management platforms. These systems integrate information from multiple inspection technologies, historical records, and geographic information systems. Advanced analytics identify trends, predict future degradation, and optimize maintenance planning.
Repair and Rehabilitation Techniques in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Effective remediation strategies address identified integrity concerns:
Composite Repair Systems for Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Engineered composite solutions have revolutionized pipeline construction and maintenance repair strategies. These systems, typically incorporating fiber-reinforced polymers with specialized adhesives, restore structural integrity without service interruption. Design methodologies consider pressure containment, external loading, and long-term performance requirements.
Hot Tapping in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
The ability to make connections to active pipelines represents an important capability in pipeline construction and maintenance. Hot tapping techniques enable branch connections, instrument installation, and bypass operations without service interruption. These procedures require specialized equipment and rigorous safety protocols to manage associated risks.
Sleeve Installation for Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Steel sleeves provide reliable reinforcement in many pipeline construction and maintenance scenarios. Type A (non-pressure containing) and Type B (pressure containing) designs address different defect types and operational requirements. Installation methodologies include welded split sleeves, mechanical clamps, and specialized configurations for complex geometries.
Line Replacement Strategies in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Complete segment replacement becomes necessary in certain pipeline construction and maintenance situations. Modern approaches often employ parallel installation with minimal service disruption. Abandonment protocols for decommissioned segments address environmental considerations and future land use requirements.
Environmental Considerations in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Responsible practices minimize ecological impact:
Erosion Control in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Preventing soil loss represents a primary environmental concern in pipeline construction and maintenance. Effective strategies include temporary measures during construction (silt fences, erosion control blankets) and permanent solutions for long-term stability (revegetation, riprap, engineered drainage). Regular monitoring ensures continued effectiveness of these control measures.
Waterbody Crossing Methods in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Pipeline construction and maintenance across streams, rivers, and wetlands requires specialized approaches. Techniques include open-cut crossing, horizontal directional drilling, and aerial spans depending on environmental sensitivity and regulatory requirements. Restoration protocols address riverbed stabilization, habitat preservation, and water quality protection.
Spill Prevention and Response in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Environmental protection in pipeline construction and maintenance encompasses comprehensive spill management. Preventative measures include secondary containment, strategic valve placement, and leak detection systems. Response planning involves equipment staging, personnel training, and coordination with regulatory agencies to minimize impacts if incidents occur.
Habitat Restoration in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Returning disturbed areas to productive ecological function represents an important aspect of pipeline construction and maintenance. Restoration approaches vary based on local ecosystems, incorporating native vegetation reestablishment, habitat enhancement features, and specialized techniques for sensitive environments. Monitoring programs track restoration success and guide adaptive management.
Digital Transformation in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Technology revolutionizes infrastructure management:
Geographic Information Systems for Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Spatial data management has transformed pipeline construction and maintenance planning and execution. GIS platforms integrate multiple data types, providing comprehensive visualization of pipeline networks with associated attributes. These systems support route planning, construction logistics, maintenance scheduling, and regulatory compliance documentation.
Remote Monitoring in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Telemetry solutions enable real-time awareness of pipeline conditions. Modern pipeline construction and maintenance programs incorporate SCADA systems, remote sensors, and communications infrastructure that transmit operational parameters, environmental conditions, and security status. These capabilities enhance both routine monitoring and emergency response.
Predictive Analytics for Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Data-driven decision making represents the frontier of pipeline construction and maintenance optimization. Advanced analytics platforms process information from multiple sources to identify potential issues before they manifest as failures. Machine learning algorithms continue to enhance predictive capabilities as they process growing datasets from operational pipelines.
Digital Twin Technology in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Virtual replicas of physical pipeline assets offer revolutionary capabilities for pipeline construction and maintenance planning. These detailed models simulate operational conditions, test maintenance scenarios, and predict outcomes of proposed modifications. Digital twin implementation continues to expand as the technology demonstrates significant value in complex infrastructure management.
Workforce Development for Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Human capital represents the foundation of infrastructure excellence:
Training Requirements for Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Comprehensive education programs ensure personnel possess the knowledge and skills required for effective pipeline construction and maintenance. Training encompasses technical aspects, safety protocols, regulatory requirements, and environmental considerations. Certification programs validate competency in specialized areas including welding, inspection, and corrosion protection.
Safety Culture in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Prioritizing worker protection and operational safety defines excellence in pipeline construction and maintenance. Effective programs incorporate hazard identification, risk assessment, protective equipment, and procedural compliance. Safety metrics tracking, near-miss reporting, and continuous improvement initiatives cultivate environments where incidents become increasingly rare.
Knowledge Transfer in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Preserving institutional knowledge represents a significant challenge in pipeline construction and maintenance. Structured approaches including documentation systems, mentoring programs, and cross-training initiatives ensure critical expertise remains available despite workforce transitions. These efforts prove particularly important as experienced personnel approach retirement age.
Technological Adaptation in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Embracing emerging tools and methodologies ensures pipeline construction and maintenance capabilities remain current. Professional development programs familiarize personnel with new equipment, software platforms, and analytical techniques. This ongoing education enables organizations to maintain competitive advantages while delivering increasingly effective infrastructure management.
Economic Considerations in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Financial factors influence infrastructure decisions:
Lifecycle Cost Analysis for Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Comprehensive economic assessment considers both initial and long-term expenditures in pipeline construction and maintenance. This approach evaluates capital costs alongside projected operational expenses, maintenance requirements, and eventual decommissioning. Lifecycle analysis often reveals that higher initial investment in quality materials and construction techniques yields substantial long-term savings.
Risk-Based Resource Allocation in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Optimizing expenditures based on potential consequences guides effective pipeline construction and maintenance strategies. This methodology directs greater resources toward pipeline segments where failures would cause significant safety, environmental, or business impacts. Risk-based approaches maximize the protective value achieved from maintenance budgets.
Regulatory Compliance Costs in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Meeting evolving standards represents a significant economic factor in pipeline construction and maintenance. Organizations must budget for both initial permitting processes and ongoing compliance activities including documentation, inspection, testing, and reporting. Proactive compliance strategies typically prove more economical than reactive approaches necessitated by regulatory findings.
Innovative Contracting Models for Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Partnership approaches between operators and service providers create value in pipeline construction and maintenance. Performance-based contracts, alliance agreements, and integrated project delivery models align incentives among stakeholders. These arrangements often accelerate project timelines while improving quality and reducing overall costs.
Future Trends in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Emerging developments shape tomorrow’s infrastructure:
Automation Advances in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Robotic systems continue transforming pipeline construction and maintenance capabilities. Automated welding technology improves consistency while reducing labor requirements. Inspection robots access confined spaces with unprecedented sensor capabilities. Development continues on fully autonomous systems capable of performing complex maintenance tasks with minimal human intervention.
Sustainable Practices in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Environmental responsibility increasingly defines excellence in pipeline construction and maintenance. Initiatives include renewable energy for pump stations, methane emission reduction, water conservation, and circular economy approaches to material recycling. These practices reduce environmental footprints while often delivering operational cost advantages.
Material Science Innovations for Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Advanced materials reshape possibilities in pipeline construction and maintenance. Developments include nanomaterial-enhanced coatings with self-healing capabilities, ultra-high-strength steels that reduce weight while increasing pressure capacity, and smart materials that change properties in response to environmental conditions. These innovations promise extended service life with reduced maintenance requirements.
Regulatory Evolution Affecting Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Shifting oversight frameworks continue influencing pipeline construction and maintenance practices. Trends include increased emphasis on risk assessment, greater scrutiny of environmental impacts, enhanced stakeholder engagement requirements, and more stringent documentation standards. Successful organizations maintain awareness of developing regulations while participating constructively in standard-setting processes.
Conclusion: Excellence in Pipeline Construction and Maintenance
Pipeline construction and maintenance represent essential disciplines that combine engineering expertise, environmental stewardship, and operational discipline. Organizations that excel in these areas recognize the interconnected nature of planning, execution, monitoring, and continuous improvement. By adopting comprehensive approaches that address technical, environmental, and human factors, pipeline operators ensure the safe and efficient transportation of vital resources.
As technology continues advancing and societal expectations evolve, pipeline construction and maintenance methodologies will undoubtedly transform. However, the fundamental principles of integrity, safety, and sustainability will remain constant. By embracing both proven practices and promising innovations, the pipeline industry will continue providing the critical infrastructure upon which modern society depends.
This exploration of pipeline construction and maintenance reflects current best practices while acknowledging the dynamic nature of this essential field. Organizations that commit to excellence in these disciplines position themselves for operational success while demonstrating responsible stewardship of both natural resources and critical infrastructure assets.